【Kotlin Compiler】IR Transform Plugin 教程
- 本文会通过一个小 demo 手把手教你学会如何利用 Kotlin Compiler Plugin 进行 IR 插桩。如果你对 IR(intermediate representation) 是什么还一知半解,不妨先参考 【Kotlin Compiler】IR 介绍
- 如果你想直接参考源码,可以直接看这里,如果能点个 star 就更好了
下面开始正题
我们的目标是什么?
先来看两段代码1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8fun foo(param1: String? = "Hello", param2: String? = "World"): String {
println("foo costs[${startTime.elapsedNow()}]")
val startTime = TimeSource.Monotonic.markNow() //类似 Java 中的 System.currentMills()
// do something cost time
val result = param1 + param2
println("foo costs[${startTime.elapsedNow()}]")
return result
}
这是我们日常通过 log 统计方法耗时的一个小例子,如果需要统计的方法数量较多,我们要手写非常多的重复代码。
在 Java 中,我们可以找到被注解标注的方法,然后通过 Transform 字节码的方式将模板代码插到指定位置。在 Kotlin 中,方案是一样的,只不过我们需要 Transform 的不是字节码了,而是 IR。做完 Transform 的工作后,只需写下面这段代码就可满足需求。
1 |
|
怎样开发一个 Kotlin Compiler Plugin?
了解完我们的目标后,就需要了解开发一个 Kotlin Compiler Plugin 的标准过程是什么?我们需要了解那些概念,要用哪些 API?
下面我们先来看看如何开发 Kotlin Compiler Plugin

此图是 Kotlin Compiler Plugin 的架构图,我已经在图中标注了每个模块的职责是什么,不再赘述。
0.工程搭建
环境说明:
- IDE-IntelliJ IDEA 2021.3.3 (Community Edition)
- KotlinPlugin-1.6.21
- JDK-1.8
下面是工程中需要依赖的库和插件,详细可参考Sample代码依赖1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16apply plugin: "java-gradle-plugin"
apply plugin: "org.jetbrains.kotlin.jvm"
apply plugin: "kotlin-kapt"
dependencies {
implementation gradleApi()
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:1.6.21") // kotlin 标准库
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-gradle-plugin-api:1.6.21") // kotlin-插件 api
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-compiler-embeddable:1.6.21") // kotlin-插件 api 注意:如果需要用 com.github.tschuchortdev:kotlin-compile-testing,这里必须使用 embeddable 版本
implementation "com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0.1" //auto-service,找到插件中的具体实现类
kapt "com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0.1" //kapt 生成映射代码
testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter:5.8.1' // junit engine
testImplementation 'org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-test-junit:1.6.21'
testImplementation("com.github.tschuchortdev:kotlin-compile-testing:1.4.8") //compiler plugin / ksp plugin 单测扩展库
}
1.KotlinCompilerPluginSupportPlugin
此类是 Gradle 和 Kotlin 的桥梁,主要职责是提供插件入口,获取插件 AGV(artifact group version)
1 | class MethodPerfIRPlugin: KotlinCompilerPluginSupportPlugin { |
重点要说的是 applyToCompilation,isApplicable 两个方法:
isApplicable比较简单,只有当其返回 true 的时候,applyToCompilation才会执行applyToCompilation重点是返回值,在build.gradle的一些自定义配置可以通过这里透传到 Kotlin Compiler Plugin 中来,方便后续使用
2.CommandLineProcessor
1 |
|
此类和 ComponentRegistrar 是我们写插件真正的入口,CommandLineProcessor 的作用是解析 cli 中的参数并保存下来,本次目标不涉及,大家有兴趣或有需求可以自己研究。
需要注意的是,此类一定要用 @AutoService 标记,否则无法调用到我们的实现
3.ComponentRegistrar
1 | // don't forget it |
此类的作用有两个:
- 使用
CommanLineProcessor中保存好的 option,本次逻辑不涉及,参考代码写法即可 - 注册
Extension,下面具体看Extension是什么
同样注意,不要忘记加 @AutoService
4.Extension
重点来了,我们 80% 的逻辑可能都写在 Extension 中,通过此类我们可以对 IR 进行增删改,具体如下
1 | class MethodPerfExtension(): IrGenerationExtension { |
此类中只有 generate 方法,其中包含两个参数:
IrModuleFragment代表 IR 树的根节点,描述的是 module 相关的信息,比如里面是一组irFile,自顶向下遍历可以得到整个 module 的 ir 信息IrPluginContext包含了大多数我们在 transform IR 时用到的 api 和信息
Dump IR 树
在 Kotlin IR 中,IrElement 是一切 IR 结构的父类,我们可以通过其扩展方法 IrElement.dump 查看 IR 树是怎样的结构。
比如,我们在 generate 中调用 moduleFragment.dump(),来查看下面代码的 IR
1 | fun main() { |
会得到
1 |
|
实现目标
了解 Kotlin Complier Plugin 的基本情况后,你应该大致清楚了开发插件的过程。下面我们通过完成目标,加深对这个过程的理解。
0.技术方案
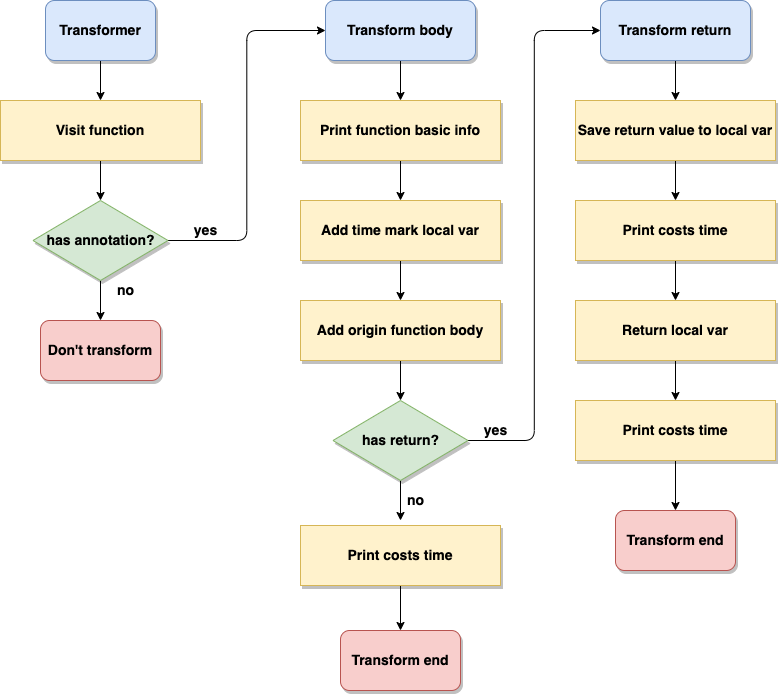
Transform 流程并不复杂,主要包含了:
- 找到加注解的方法
- 重写方法体 IR
a. 增加时间戳
b. 原始方法体
c. 统计耗时 - 如果方法包含返回值,需要先保存返回值,再进行统计耗时
1.开发 IrElementTransformer
IrElementTransformer 继承自 IrElementVisitor,功能类似,不再赘述。
直接看一下代码,我们在 IrElementTransformer 中做了什么1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14class MethodCostTimeTransformer(
private val pluginContext: IrPluginContext
): IrElementTransformerVoidWithContext() {
override fun visitFunctionNew(declaration: IrFunction): IrStatement {
println("visitFunctionNew:: ${declaration.render()}")
val body = declaration.body
val annotationClass = pluginContext.referenceClass(FqName("com.zzt.demo.annotation.Cost"))!!
if (body != null && declaration.hasAnnotation(annotationClass)) { //有方法体&被注解标注的方法
declaration.body = irCost(declaration, body) //transform 方法体
}
return super.visitFunctionNew(declaration)
}
}
逻辑比较清晰,找到我们定义的注解,看被 visit 的方法是否加了注解,如果加了,就调用 irCost() Transform 方法体 IR
下面看看 irCost() 做了什么1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18private fun irCost(
irFunction: IrFunction,
irBody: IrBody): IrBlockBody {
println("irCost:: ")
return DeclarationIrBuilder(pluginContext, irFunction.symbol).irBlockBody {
+costEnter(pluginContext, irFunction) //打印目标函数信息
val startTime = irTemporary(irCall(pluginContext.markNowFunc()).also {
it.dispatchReceiver = irGetObject(pluginContext.monotonicClass())
}) // 相当于调用 TimeSource.Monotonic.markNow()
+irBlock(resultType = irFunction.returnType) {
for(statement in irBody.statements) { //原有方法体中的表达式
+statement
}
}.transform(CostTimeReturnTransformer(pluginContext, irFunction, startTime), null)
}
}
- 在方法耗时统计之前,通过
costEnter()插桩打印目标函数的信息,比如方法名,参数是什么 - 调用
TimeSource.Monotonic.markNow()记录开始时间 startTime - 追加原有方法体内容,并开始进行返回体的 Transform
2. CostTimeReturnTransformer
1 | class CostTimeReturnTransformer( |
上述代码逻辑也比较清晰
- 如果不是目标函数,直接 return
- 如果目标函数无返回值,直接插桩
costExit() - 如果有返回值,则需要先保存返回值到临时变量,然后再插桩
costExit(),并且要补上原有的返回值,否则会造成方法一直返回 null 的情况
3. 测试
https://github.com/tschuchortdev/kotlin-compile-testing 此库专用于 Kotlin Compiler Plugin 或者 KSP Plugin 的单测,让我们不需要将插件集成到目标工程就能进行测试,且容易上手,推荐大家使用。
但目前有个库兼容问题需要注意,我们在开发插件时必须依赖 implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-compiler-embeddable:1.6.21"),不能使用 implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-compiler:1.6.21")
下面就看看如何进行测试
1 | class MethodPerfTest { |
- 通过
SourceFile.kotlin或SourceFile.fromPath()可以传入需要测试的代码 - 测试代码会通过集成了
MethodPerfComponentRegistrar的 kt 编译器进行编译 - 通过类加载目标代码,反射调用 main 函数,看执行结果是否正确
下面看看 Transform IR 的结果
1 | ⇢ foo(param1=Hello, param2=World) |


